|
Size: 5089
Comment:
|
Size: 7141
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| ||<(^|2>'''Dozenten:''' || [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~brefeld|Dr. Ulf Brefeld]], [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai|Dr. Marc Toussaint]] || | ||<(^|2>'''Dozenten:''' || [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai|Dr. Marc Toussaint]], [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~brefeld|Dr. Ulf Brefeld]] || |
| Line 50: | Line 50: |
| === Projekte === * [[attachment:dialogProjekt.pdf|Projektskizze]] fuer eine '''Diplom/MSc-Arbeit''' |
|
| Line 54: | Line 57: |
| || 28.04. || (konditionale) Unabhängigkeit, Bayesische Netzwerke, Inferenz, Beispiele || [[attachment:02.pdf|vl02]] [[attachment:02_4up.pdf|vl02_4up]] || [[attachment:ex2.pdf|ex2]] || || 05.05. || Faktorgraphen, Eliminierungsalgorithmus, Belief Propagation || [[attachment:03.pdf|vl03]] [[attachment:03_4up.pdf|vl03_4up]] || [[attachment:ex3.pdf|ex3]] [[attachment:hmm.tgz|code]] || || 12.05. || Beispiele: HMMs, Markov Random Fields; building Junction Trees || [[attachment:04.pdf|vl04]] [[attachment:04_4up.pdf|vl04_4up]] [[attachment:hmm-bin.tgz|code]] || [[attachment:ex4.pdf|ex4]] || || 19.05. || Lernen & Likelihood Maximization || [[attachment:05.pdf|vl05]] [[attachment:05_4up.pdf|vl05_4up]] || [[attachment:ex5.pdf|ex5]] || |
|
| Line 55: | Line 62: |
| || 28.04. || Graphische Modelle, Faktorgraphen, Inferenz || || [[attachment:ex2.pdf|ex2]] || || 05.05. || Inferenz, Eliminierungsalgorithmus, Evidenzen || || || || 12.05. || Summen-Produkt-Algorithmus, Junction Tree Alg. (JTA) || || || || 19.05. || Beliefpropagierung in zyklischen Graphen (Loopy BP), Mean-Field Alg. || || || |
|| 26.05. || HMMs, Forward-Backward, Viterbi, Expectation-Maximization, (Kernel-) Conditional Random Fields, Features || [[attachment:06.pdf|vl06]] [[attachment:06_4up.pdf|vl06_4up]] || [[attachment:ex6.pdf|ex6]] || || 09.06. || CRF-Optimierung, Strukturiertes Perzeptron || [[attachment:07.pdf|vl07]] [[attachment:07_4up.pdf|vl07_4up]] || [[attachment:ex7.pdf|ex7]] [[attachment:esp.data2_10-40|data]] || || 16.06. || Perzeptron, Strukturierte Support-Vektor-Maschinen (SSVMs) || [[attachment:08.pdf|vl08]] [[attachment:08_4up.pdf|vl08_4up]] || frei || || 23.06. || Strukturierte Support-Vektor-Maschinen (SSVMs) || [[attachment:09.pdf|vl09]] [[attachment:09_4up.pdf|vl09_4up]] || [[attachment:ex9.pdf|ex9]] || |
| Line 60: | Line 67: |
| || 26.05. || Hidden Markov Models (HMMs), Forward-Backward Alg., Viterbi, Expectation-Maximization (EM) || || || || 02.06. || Bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeiten, (Kernel-) Conditional Random Fields (k-CRFs), Features, Optimierung || || || || 09.06. || Optimierung (Fortsetzung), Strukturiertes Perzeptron || || || || 16.06. || Strukturierte Support-Vektor-Maschinen (SSVMs) || || || || || || || || || 23.06. || Influence Diagramme || || || || 30.06. || Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) || || || || 07.07. || Inferenz für Planen, Optimale Handlungsanweisungen (Policies) || || || |
|| 30.06. || Learning with missing data, Expectation Maximization || [[attachment:10.pdf|vl10]] [[attachment:10_4up.pdf|vl10_4up]] || [[attachment:ex10.pdf|ex10]] || || 07.07. || Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), EM für optimale Handlungsanweisungen (Policies) || [[attachment:11.pdf|vl11]] [[attachment:11_4up.pdf|vl11_4up]] || [[attachment:ex11.pdf|ex11]] || |
| Line 69: | Line 70: |
| || 14.07. || Zusammenfassung und Fragestunde || || || | || 14.07. || Zusammenfassung, Offene Probleme || [[attachment:12.pdf|vl12]] || || |
| Line 71: | Line 72: |
| === extra material === | === recommended reading === |
| Line 73: | Line 74: |
| * [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai/notes/belief-propagation.pdf|lecture notes on factor graphs and belief propagation]] | * on inference in general: * [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai/notes/belief-propagation.pdf|lecture notes on factor graphs and belief propagation]] * Bishop: [[attachment:bishop-chapter8.pdf|Chapter 8 of his book]], [[attachment:bishop-chapter8.pdf|corresponding lecture slides]] * !MacKay: [[http://www.inference.phy.cam.ac.uk/itprnn/book.html|Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms]] |
| Line 75: | Line 79: |
| === web material === | * on Bayes rule and Bayesian networks: * Bayes Rule: [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes/bayesrule.html]] * [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes/Charniak_91.pdf|Charniak: "Bayesian Networks without Tears"]] |
| Line 77: | Line 83: |
| * Bayes Rule: [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes/bayesrule.html]] * [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes/Charniak_91.pdf|Charniak: "Bayesian Networks without Tears"]] * [[http://research.microsoft.com/apps/pubs/default.aspx?id=69588|Heckerman: A Tutorial on Learning With Bayesian Networks]] * Kevin's lecture: [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Teaching/CS532c_Fall04/Lectures/index.html]], his notes on Bayes etc [[http://www.google.de/search?q=site:www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes]] * inference software: [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai/links.html]] and [[http://www.stat.duke.edu/courses/Spring99/sta294/sw.html]] * Max Welling's class notes [[http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/classnotes/classnotes.html]] |
* related lectures: * Kevin Murphy's lecture: [[http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Teaching/CS532c_Fall04/Lectures/index.html]], his notes on Bayes etc [[http://www.google.de/search?q=site:www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes]] * Max Welling's class notes [[http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/classnotes/classnotes.html]] * Chris Williams' PRM lecture: [[http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/pmr/]] * Zoubin Ghahramani's tutorials and teaching material: [[http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/]] * on learning: * [[http://research.microsoft.com/apps/pubs/default.aspx?id=69588|Heckerman: A Tutorial on Learning With Bayesian Networks]] * [[http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/bayesian.html|Zoubin Ghahramani: Bayesian Machine Learning]] * Davis and Jones, ML Estimation for the Multinomial Distribution, Teaching Statistics 14(3), 1992 [[http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/119984860/PDFSTART]] * software: * inference software: [[http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai/links.html]] and [[http://www.stat.duke.edu/courses/Spring99/sta294/sw.html]] * [[http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~javabayes/Home/|JavaBayes software]] -- directly test the [[http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~javabayes/Home/applet.html|online java applet]] |
Describe Main/SS09_GraphicalModels here.
Vorlesung "Einführung in Graphische Modelle"
Vorlesung:
Dienstag 14.00-16.00
FR-6535
Übung:
Dienstag 16.00-18.00
FR-4061
Dozenten:
Tobias Lang (Übung)
Inhalt
Graphische Modelle definieren Warscheinlichkeitsfunktionen auf gekoppelten Variablen. Die gerichtete oder ungerichtete Graphstruktur erlaubt somit eine sehr flexible Modellierung von Variablen (=Knoten) und Anhängigkeiten zwischen Variablen (=Kanten).
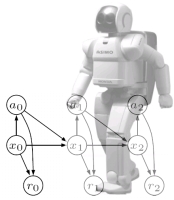
In den letzten Jahren wurden eine Reihe sehr mächtiger Inferenzalgorithmen (z.B. Viterbi Algorithmus, Junction Tree Algorithmus) entwickelt, die es uns erlauben graphische Modelle direkt für die Modellierung von natürlich auftretender Problemstellungen zu nutzen. Sie werden beispielsweise in der Handlungsplanung von Robotern und der maschinellen Sprach- und Bildverarbeitung erfolgreich eingesetzt. Desweiteren basieren viele aktuelle Verfahren des maschinellen Lernens wie z.B. Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Conditional Random Fields (CRFs) oder Structured Support Vector Machines (SSVM) auf graphischen Modellen.
Die Vorlesung führt in die Grundlagen Graphischer Modelle ein und stellt sie anhand von praktischen Beispielen aus den genannten Gebieten (Robotik, Sprach- und Bildverarbeitung) vor. Thematisch beginnen wir mit einfachen Bayesschen Netzwerken, lernen dann verschiedene Inferenzmechanismen kennen und leiten schliesslich aktuelle Lernverfahren wie HMMs, CRFs und SSVMs her. Am Ende sollen die Teilnehmer in der Lage sein, beliebige Problemstellungen mit Hilfe von graphischen Modellen zu kodieren und zu lösen.
Voraussetzungen
gute Mathematikkenntnisse; Statistikkenntnisse sind nützlich, aber nicht zwingend erforderlich.
Übung
Es gibt jede Woche ein Übungsblatt. Voraussetzung zur Teilnahme an der Prüfung am Semesterende ist die erfolgreiche Bearbeitung der Hälfte aller Übungsaufgaben. Erfolgreiche Bearbeitung bedeutet, dass es ersichtlich wird, dass man sich mit der Aufgabe auseinandergesetzt und die zugrundeliegenden Themen prinzipiell verstanden hat. Blätter sind einzeln zu bearbeiten. Zu Beginn jeder Übung ist auf einer Liste anzukreuzen, welche Aufgaben man bearbeitet hat. Unter den möglichen Kandidaten wird einer per Zufall bestimmt, der die Aufgabe an der Tafel vorrechnet. Falls man an der Teilnahme der Übung verhindert ist, kann man ausnahmsweise seine Bearbeitung in der Vorlesung zuvor abgeben.
Projekte
Projektskizze fuer eine Diplom/MSc-Arbeit
Termine
Datum
Beschreibung
Vorlesung
Übung
21.04.
Einführung mit Überblick (Motivation, Zufallsvariablen, Bedingte und Verbundwahrscheinlichkeit, Bayes)
28.04.
(konditionale) Unabhängigkeit, Bayesische Netzwerke, Inferenz, Beispiele
05.05.
Faktorgraphen, Eliminierungsalgorithmus, Belief Propagation
12.05.
Beispiele: HMMs, Markov Random Fields; building Junction Trees
19.05.
Lernen & Likelihood Maximization
26.05.
HMMs, Forward-Backward, Viterbi, Expectation-Maximization, (Kernel-) Conditional Random Fields, Features
09.06.
CRF-Optimierung, Strukturiertes Perzeptron
16.06.
Perzeptron, Strukturierte Support-Vektor-Maschinen (SSVMs)
frei
23.06.
Strukturierte Support-Vektor-Maschinen (SSVMs)
30.06.
Learning with missing data, Expectation Maximization
07.07.
Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), EM für optimale Handlungsanweisungen (Policies)
14.07.
Zusammenfassung, Offene Probleme
recommended reading
- on inference in general:
- on Bayes rule and Bayesian networks:
- related lectures:
Kevin Murphy's lecture: http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Teaching/CS532c_Fall04/Lectures/index.html, his notes on Bayes etc http://www.google.de/search?q=site:www.cs.ubc.ca/~murphyk/Bayes
Max Welling's class notes http://www.ics.uci.edu/~welling/classnotes/classnotes.html
Chris Williams' PRM lecture: http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/pmr/
Zoubin Ghahramani's tutorials and teaching material: http://learning.eng.cam.ac.uk/zoubin/
- on learning:
Davis and Jones, ML Estimation for the Multinomial Distribution, Teaching Statistics 14(3), 1992 http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/119984860/PDFSTART
- software:
inference software: http://user.cs.tu-berlin.de/~mtoussai/links.html and http://www.stat.duke.edu/courses/Spring99/sta294/sw.html
JavaBayes software -- directly test the online java applet